| Bloc | Core bloc library |
|---|---|
Flutter_bloc | Fast, responsive Flutter Widgets built to work with bloc in mobile applications. |
angular_bloc | Rich, fast, and reactive Angular Components built to work with bloc to build lightning-fast applications. |
Hydrated_bloc | Added support for persisting and restoring bloc states to the state management library. |
Replay_bloc | Includes undo and redo functionality for the bloc state management library. |
What Is Flutter Bloc?
In Flutter applications, the Flutter BLoC is used to manage the state. The flutter state management feature allows handling all possible states of the application easily. It is easy to grasp the concept of the Flutter bloc. This library has excellent documentation with a lot of examples. It's also one of the most commonly used libraries in the Flutter community.
It is powerful since it allows the creation of all kinds of applications. For instance, the Flutter bloc is appropriate in both production and learning environments.
Flutter Bloc: An Overview
There are several pub packages included in the Bloc:
It is necessary to install the Dart SDK on the computer before one can use bloc.
Installation
First, our pubspec.yaml needs to include the bloc package as a dependency for a Dart application.

As a dependency, the flutter_bloc package needs to be added to pubspec.yaml for a Flutter application.

Similarly, as a dependency, the angular_bloc package needs to be added to pubspec.yaml for an AngularDart application.

The next step is to install Bloc.
If it does not have a pubspec.yaml file, make sure to run this command from the same directory as pubspec.yaml.
- If using Dart or AngularDart, run pub get
- If using Flutter, then run flutter packages get
Import
We can now import bloc into main.dart after successfully installing bloc.

Bloc
A Bloc is a more advanced class that incorporates events rather than functions to trigger state changes. Unlike Cubit, Bloc also extends BlocBase, which means its API is similar. A Bloc receives an event, which then changes the incoming event into an outgoing state rather than directly calling a function on the Bloc and emitting a new state.
Creating A Bloc
A Bloc can be created to specify what events it will process. Blocs receive events as input. They are often added when users interact with a page, such as by pressing buttons. As with Blocs, Cubits also define the state they will manage.

The superclass must also be passed an initial state, just as when creating the CounterCubit.
State Changes
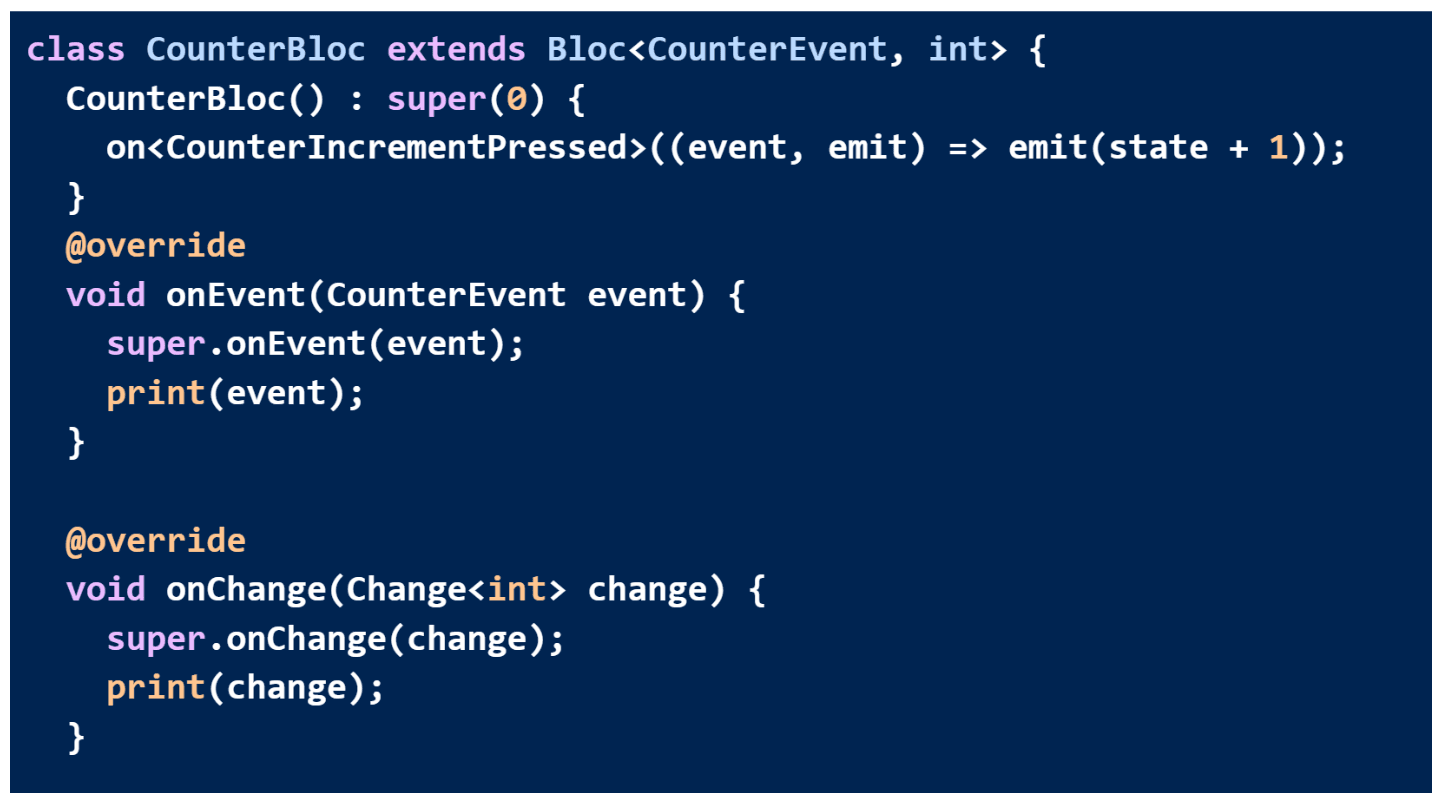
In Bloc, event handlers are registered using the on<Event> API. Any incoming event is converted into one or more outgoing states by an event handler.

The EventHandler can then be updated to handle CounterIncrementPressed
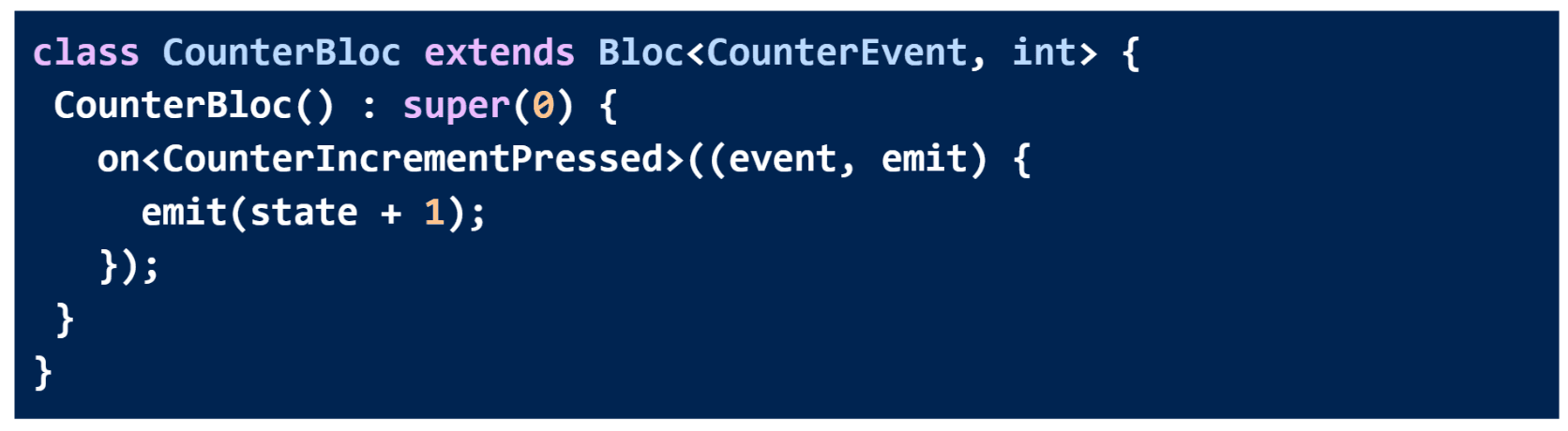
In the above snippet, we are registering an EventHandler to handle CounterIncrementPressed events. A state getter and emit(state + 1) are available to access the current bloc state for an incoming CounterIncrementPressed event.
Using a Bloc
Let's create a CounterBloc instance and use it!
Basic Usage

As shown in the above code snippet, we create a CounterBloc instance. This is the initial state of the Bloc, since no new states have yet been emitted. After that, we add the CounterIncrementPressed event to signal a change in state. Lastly, we close the internal state stream on the Bloc by printing the state of the Bloc, which has changed from 0 to 1.
Stream Usage
Just like with Cubit, a Bloc is a special type of Stream, which means we can also subscribe to a Bloc for real-time updates to its state:

Using the above snippet, we're subscribing to the CounterBloc and calling print on every change in state. We then add a CounterIncrementPressed event which triggers an on<CounterIncrementPressed>event handler and emits a new state. In the end, we call to cancel the subscription and close the bloc when we no longer require updates.
Observing A Bloc
Bloc is an extension of BlocBase, which means we can observe all changes to a Bloc's state using onChange.

Using main.dart, we can update it to:

Running the above snippet will produce the following output:
Change { currentState: 0, nextState: 1 }
We are able to capture information about what triggered a state change in Bloc because it is event-driven, which makes it unique from Cubit.
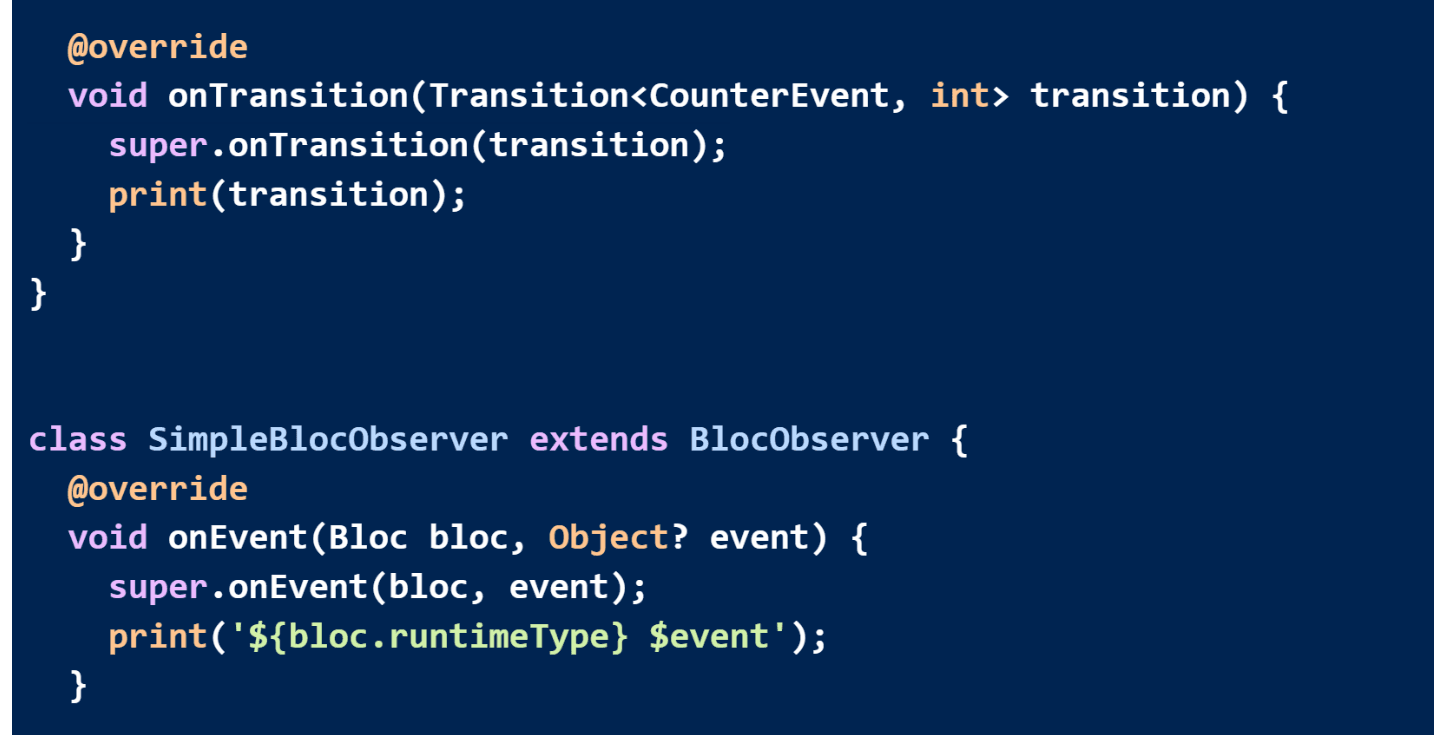
By overriding onTransition, we can accomplish this.
It is called a transition when one state changes to another. There are three types of transitions: the current state, the event, and the next state.
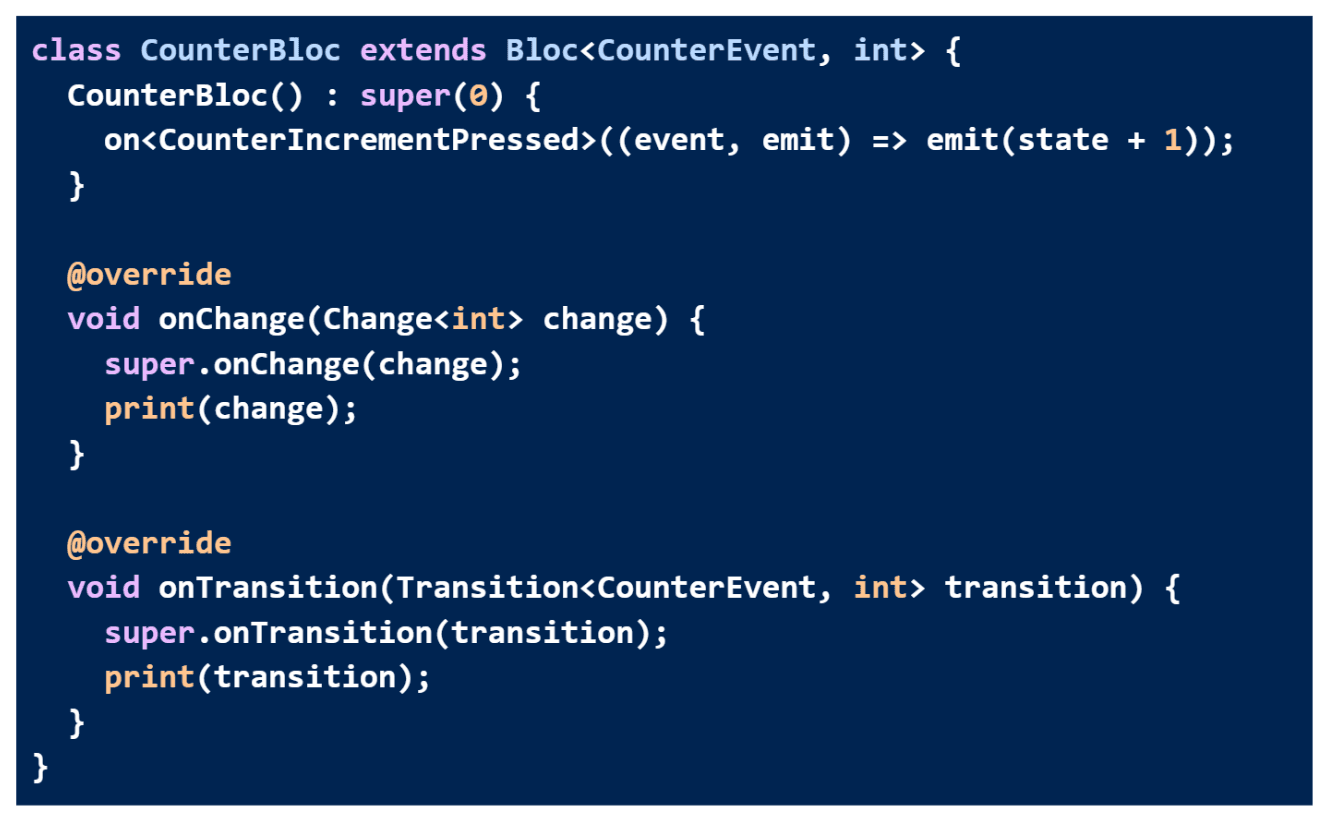
We should now see the following output if we run the same main.dart snippet again:
Transition { currentState: 0, event: Increment, nextState: 1 } Change { currentState: 0, nextState: 1 }
BlocObserver
In the same way as before, a custom BlocObserver can override onTransition to watch all transitions in one place.
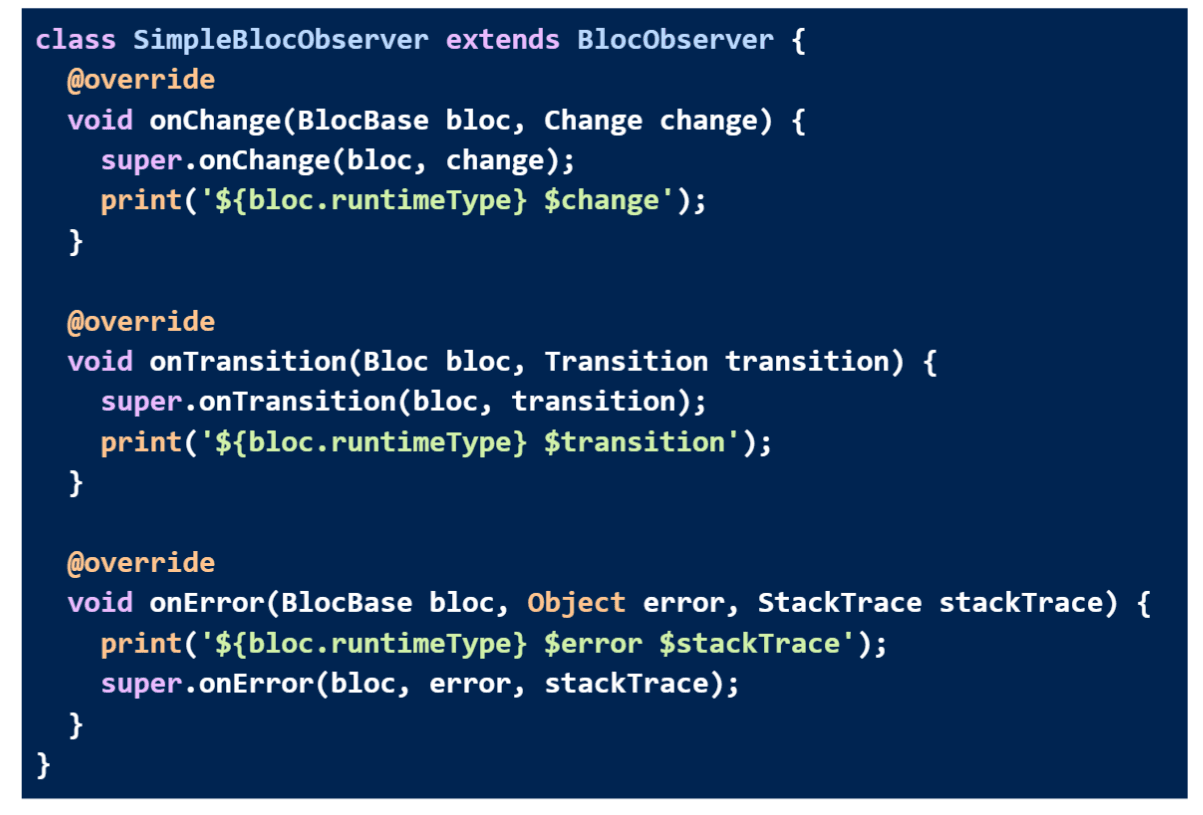
As before, we can initialize the SimpleBlocObserver as follows:

Upon running the above snippet, we should see the following output:
Transition { currentState: 0, event: Increment, nextState: 1 } CounterBloc Transition { currentState: 0, event: Increment, nextState: 1 } Change { currentState: 0, nextState: 1 } CounterBloc Change { currentState: 0, nextState: 1 }
The Bloc instance also provides us with the ability to override onEvent, which is called whenever a new event is added to the Bloc. The same goes for onChange and onTransition.


Running main.dart again should produce the following result:
Increment CounterBloc Increment Transition { currentState: 0, event: Increment, nextState: 1 } CounterBloc Transition { currentState: 0, event: Increment, nextState: 1 } Change { currentState: 0, nextState: 1 } CounterBloc Change { currentState: 0, nextState: 1 }
Flutter Bloc Tutorial For Timer
The following tutorials provide detailed instructions on how to build time, counter, login, weather, and a lot more apps using Flutter's Bloc library. These tutorials are worth checking out:
Also, Read: Flutter Tutorial for Beginners
Conclusion
For further learning, we suggest reading the detailed documentation. In addition, don't forget to check out the example tutorials given in the blog. Using good state management is essential when building flutter applications.
To summarize, Flutter is great because it's understandable and not complicated to use. It also has a lot of management options for views or widgets.